What is the full meaning of tampon?
Tampons are internal menstrual hygiene products that offer convenience and flexibility. However, correct usage and awareness of precautions are essential. This guide will provide a complete overview of tampons, from basic knowledge and usage tips to advantages, disadvantages, and safety measures.
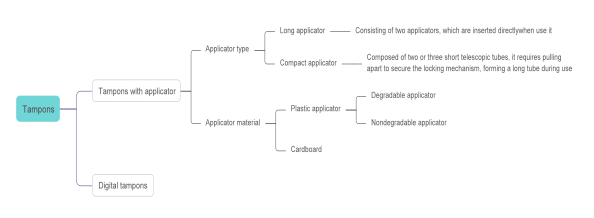
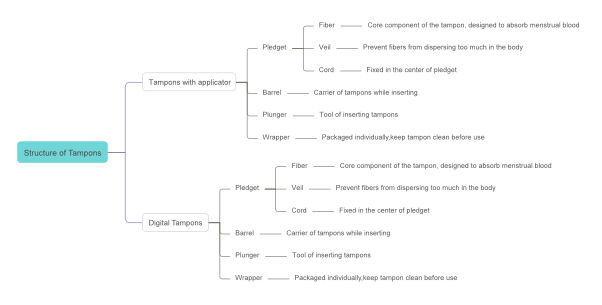
Definition&Categorization
Tampons, also known as sanitary pessaries, are cylinders made of cotton fibers, viscose fibers, or a mixture of these two types of fibers, with a drawstring attached to the end, which can be inserted into the vagina to absorb menstrual blood during a woman’s period, and can be used in place of sanitary towels, as a kind of sanitary product used by women during menstruation.
A common category:





-250x300.png)


tampon sizes
Common model
According to the US FDA standards, tampon models and absorbency are standardized and mainly classified as L, R/N, S, and SP (or S+).
tampon sizes chart
| Model | Model Description | Absorbency | VS Sanitary Towel |
| L | Mini/Light/Lite | <6g | ≈180mm sanitary towel |
| R/N | Regular/Normal | 6~9g | ≈240mm sanitary towel |
| S | Super | 9~12g | ≈280mm sanitary towel |
| SP/S+ | Super Plus/Super+ | 12~15g | ≈340mm sanitary towel |
Tampon VS Sanitary Towel
Advantages
More secure;
Butterfly cut cotton core, clover fiber imported from Europe, small volume, large suction.
Private;
Small size, very convenient to carry.
No odor and not stuffy;
Tampons are more absorbent, and the menstrual blood is absorbed immediately when the menstrual blood is discharged, ensuring that the intimate parts are dry and comfortable.
Fearless exercise;
Tampons can be used for all kinds of exercise without fear of leakage.
Product Advantages
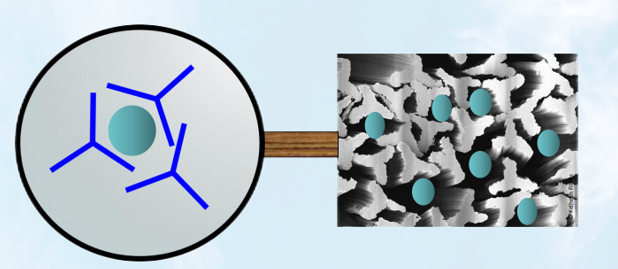
Fiber Advantage
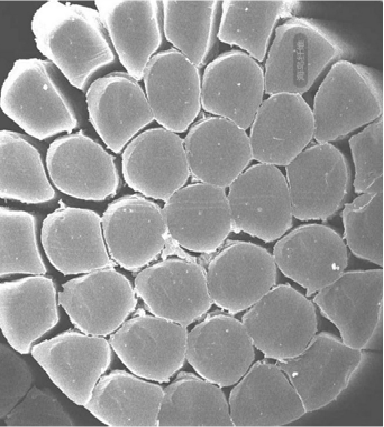
The cross-section of ordinary fibers is regular, the holding force is poor, and the compressible space is small..
We adopt imported fiber: Imported fiber with irregular cross-section, stronger holding force, greater compression rate, smaller absorber, which use of more easily inserted, and absorption is also more rapid.
OEM Tampon Service
| Model | Diameter(mm) | Length(mm) | Dry weight (g) | FDA standard absorbed amount(g) |
| L(Light) | 14 | 160 | 1.5 | <6 |
| R(Regular/Normal) | 14 | 160 | 2.2 | 6~9 |
| S(Super) | 16 | 160 | 2.7 | 9~12 |
| SP(Super plus) | 16 | 160 | 3.0 | 12~15 |

Customized solutions for tampons with an applicator
| Product type | Sorbent | Color of applicator | Material of the applicator | Cord | Color of wrapper | Material of wrapper | Absorbency requirements |
| General Products | 100% viscose | pantone:190C | plastic | cotton | PE | FDA | |
| 100% cotton | pantone:190C | plastic | cotton | PE | FDA | ||
| 100% organic cotton | pantone:190C | plastic | cotton | PE | FDA | ||
| Customized | Customized | Customized | Customized | Customized | Customized | Customized | FDA |

bulk tampons plastic applicator
| Product type | Sorbent Material | Cord | Wrapper color | Wrapper material | Absorbency requirements |
| General Products | Viscose | Cotton | As general products(Customized) | OPP/CPP | FDA |
| Customized | Customized | Customized | Customized | Customized | FDA |

Product Safety Programs Available
EO
Sterilisation Advantage
Sterilize all microorganisms, including bacterial spores.
Ability to penetrate and sterilize irregularly shaped objects
Sterilized items can be wrapped and encapsulated to maintain sterility until use.
EO does not corrode plastics, metals, or rubber, and does not cause items to become yellow or brittle.
It can be used to sterilize items that cannot be sterilized by disinfectant immersion, dry heat, pressure steam, or other chemical gases.
How to use a tampon
1. Choose the right tampon
- Tampons come in different absorbencies: light, regular, super, or super plus.
- Choose based on your flow. Start with regular if you’re a beginner.
2. Wash your hands
- Always wash your hands before and after inserting a tampon to prevent infection.
3. Get comfortable
- You can sit on the toilet, stand with one leg raised, or squat. Find a position that feels relaxed.
- Relax your muscles—tension can make insertion harder.
4. Prepare the tampon
- Remove it from its wrapper.
- If it’s an applicator tampon, hold it with your thumb and middle finger at the grip.
- If it’s a non-applicator tampon, hold it at the base where the string is attached.
5. Insert the tampon
With applicator:
- Place the tip at your vaginal opening.
- Gently push the inner tube with your index finger until the outer tube reaches your body.
- Pull out the applicator, leaving the tampon inside.
Without applicator:
- Use your finger to gently push the tampon into the vagina until it feels comfortable.
- The string should hang outside for easy removal.
6. Check comfort
- If you feel discomfort, it may not be far enough. Remove and try again with a new tampon.
- Once inserted properly, you shouldn’t feel it.
7. How long to leave it in
- Change every 4–8 hours depending on your flow.
- Never leave a tampon in for more than 8 hours to reduce the risk of TSS (toxic shock syndrome).
8. Remove the tampon
- Wash your hands.
- Gently pull the string straight out.
- Wrap it in toilet paper and throw it in the trash.
- Do not flush unless it’s labeled flushable.
9. Tips for first-timers
- Relax and take your time.
- Try a smaller or lighter tampon first.
- Stand or sit in a way that opens your vaginal canal naturally.
- Breathe deeply to reduce tension.
